
Australia’s carbon and renewable energy markets moved again this quarter, and the latest Quarterly Carbon Market Report from the Clean Energy Regulator shows just how quickly storage, certificates and renewable supply are reshaping the landscape heading into 2026. For large C&I and multi-site organisations, the shift is well underway and the decisions around energy and carbon management are becoming more strategic.
Here’s what leaders need to know.

Source: CER Quarterly Carbon Market Report, Figure 3.1
The Cheaper Home Batteries Program has moved faster than anyone expected.
This level of distributed storage is now larger than Australia’s five biggest grid-scale batteries combined, and could influence future reliability, price shape and the curve of minimum demand.
For business, this signals a future where aggregated household storage becomes a material part of system stability. This is a shift that will influence hedging costs, daytime pricing and the shape of evening peaks.
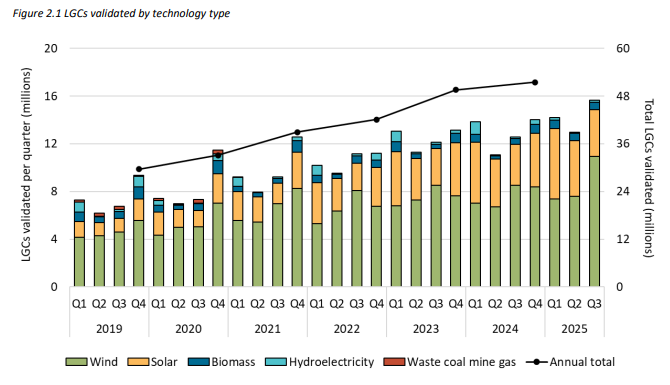
Source: CER Quarterly Carbon Market Report, Figure 2.1
Large-scale renewable generation set multiple records:
Wind and solar output lifted materially from 2024, and grid-scale solar rose 16% year-on-year in Q3.
This strengthens the supply outlook but increases exposure to weather-driven volatility – a growing factor for retailers’ appetite, tender timing, and contract structures.
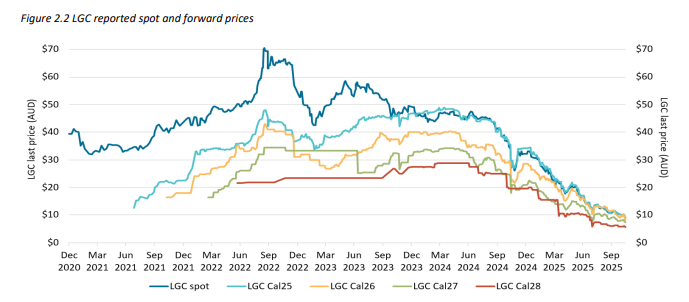
Source: CER Quarterly Carbon Market Report, Figure 2.2
Even with the highest supply on record:
Nearly half of all voluntary cancellations came from NGER reporters shifting to market-based scope 2 accounting.
Low prices are likely to drive more voluntary action in 2026 – good news for corporates aiming for 100% renewables, but a reminder that LGC procurement needs to be timed strategically.
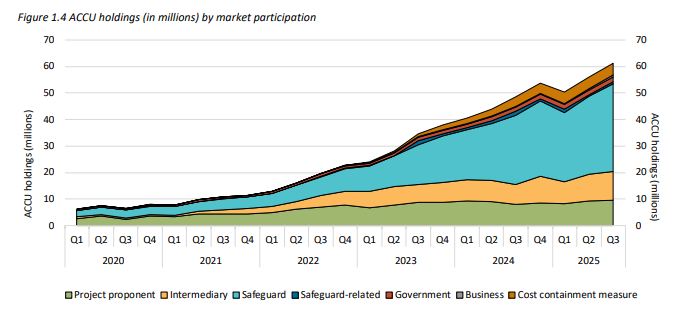
Source: CER Quarterly Carbon Market Report, Figure 1.4
Key movements in the ACCU and Safeguard Mechanism markets:
Most importantly, the ACCU price increased through the quarter, driven by safeguard entities consolidating holdings ahead of future declines in baselines.
Expect tighter ACCU markets later this decade as demand rises faster than supply.
Two major integrity frameworks went live or advanced this quarter:
For businesses, this means more credible claims – but also more complexity in certificate procurement and reporting.
For many complex C&I organisations, the challenge isn’t the contract itself – it is timing, structure, retailer appetite and the moving parts around every decision.
The data from this quarter reinforces why strategy matters:
With so many variables shifting at once – storage uptake, certificate prices, retailer appetite and compliance settings – the challenge for complex energy users isn’t the information or data itself, but knowing what to do with it.
That’s where Utilizer comes in. We interpret these signals and turn them into clear recommendations on timing, structure and risk so your decisions stay anchored, not reactive. Reach out and talk to one of our energy experts about your carbon and renewable certificate strategy for 2026.
Heatwaves and the Energy Market
January 13, 2026
Explore our monthly market wraps for a comprehensive outlook on the Australian energy market, and start making smarter energy decisions.